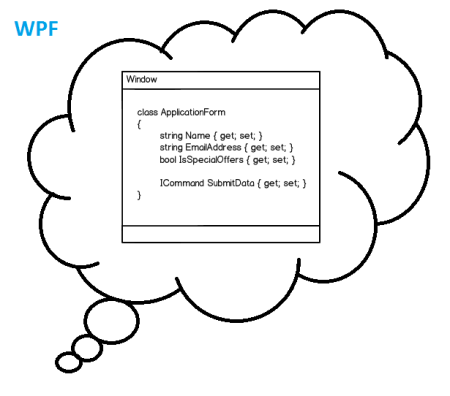
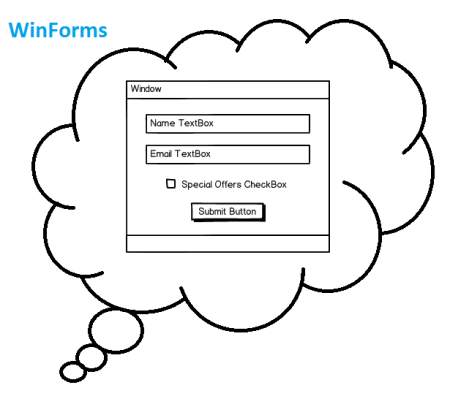
Well although, some people don't agree, I would also recomment to not use the VS designer. At least not to create an interface. If you may want to get a first impression of your implementation without starting the application, it's a good viewer at least as long no sophisticated things like Styles and Templates are used. But, IMHO, its drag and drop result should only be used as prototype and therefore be discarded after it's no longer needed.
Here are some reasons which are important for me not to use it.
The VS designer is working with fix margins and alignments (which is usually not necessary, if you're using the layout controls), means you have to touch many controls, if the requirements are changed. If you're deep in XAML and the WPF mechanics you can create an applications which can be modified with small effort, regarding the look and feel.
Since the designer is generating the xaml, the composition is not optimal and the UI may perform badly. I didn't measure it, it's just a feeling.
A much better alternative is MS Blend, although the start is everything else but easy. Its drag and drop result is much better that the result of the VS designer.
But it's a pretty powerful tool, which helps you to use pretty powerful elements to create a state of the art UI. I recommend to visit at least a short workshop to get an idea of its opportunities.
Back to your question, IMHO, and I think many people agree, get yourself a good book e.g. WPF Unleashed and later, if you want to know more about the details, WPF Pro. There are a lot of features which are different to Winforms. You won't get to know them by using any designer. I think that's the best approach.
Please also consider that there are many frameworks and libraries (e.g. MVVM light, WPFToolkit) out there, which are already solving some common problems. So it's not necessary to reinvent the wheel.